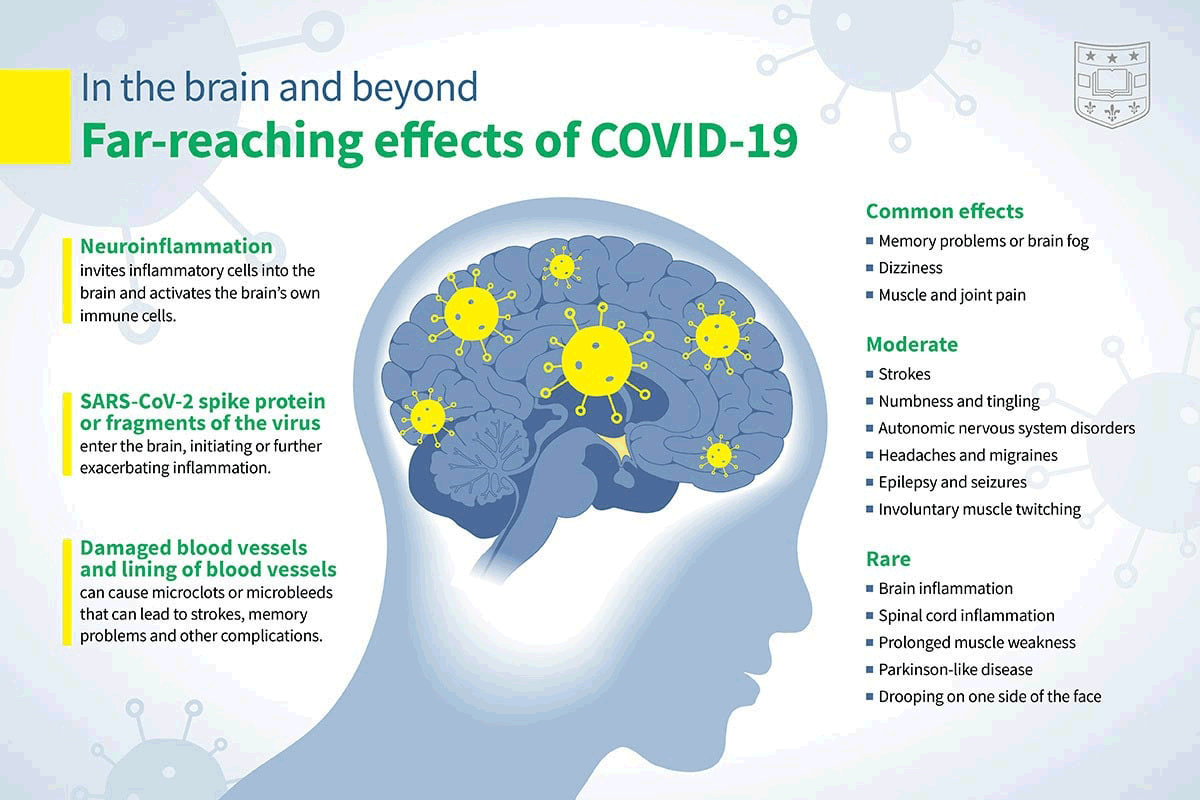
📖 SARS-CoV-2 infection of thymus induces loss of function that correlates with disease severity
❦ Lymphopenia, particularly when restricted to the T-cell compartment, has been described as one of the major clinical hallmarks in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) and proposed as an indicator of disease severity.
Although several mechanisms fostering COVID-19-related lymphopenia have been described, including cell apoptosis and tissue homing, the underlying causes of the decline in T-cell count and function are still not completely understood.
Patients with COVID-19 had reduced thymic function that was inversely associated with the severity of the disease.
Our data demonstrate that the human thymus is a target of SARS-CoV-2 and thymic function is altered following infection.
Note: Lymphopenia (also called lymphocytopenia) is a disorder in which your blood doesn't have enough white blood cells called lymphocytes. Lymphocytes play a protective role in your immune system.
❂
📖 (7 Feb 2023 ~ Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology) SARS-CoV-2 infection of thymus induces loss of function that correlates with disease severity ➤
© 2023 Rosichini et al / Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology.