📖 Health & Safety At Work Act 1974
✻ Accessed: 4 Dec 2023.
❦ The Health & Safety At Work Act (1974) [Abridged].
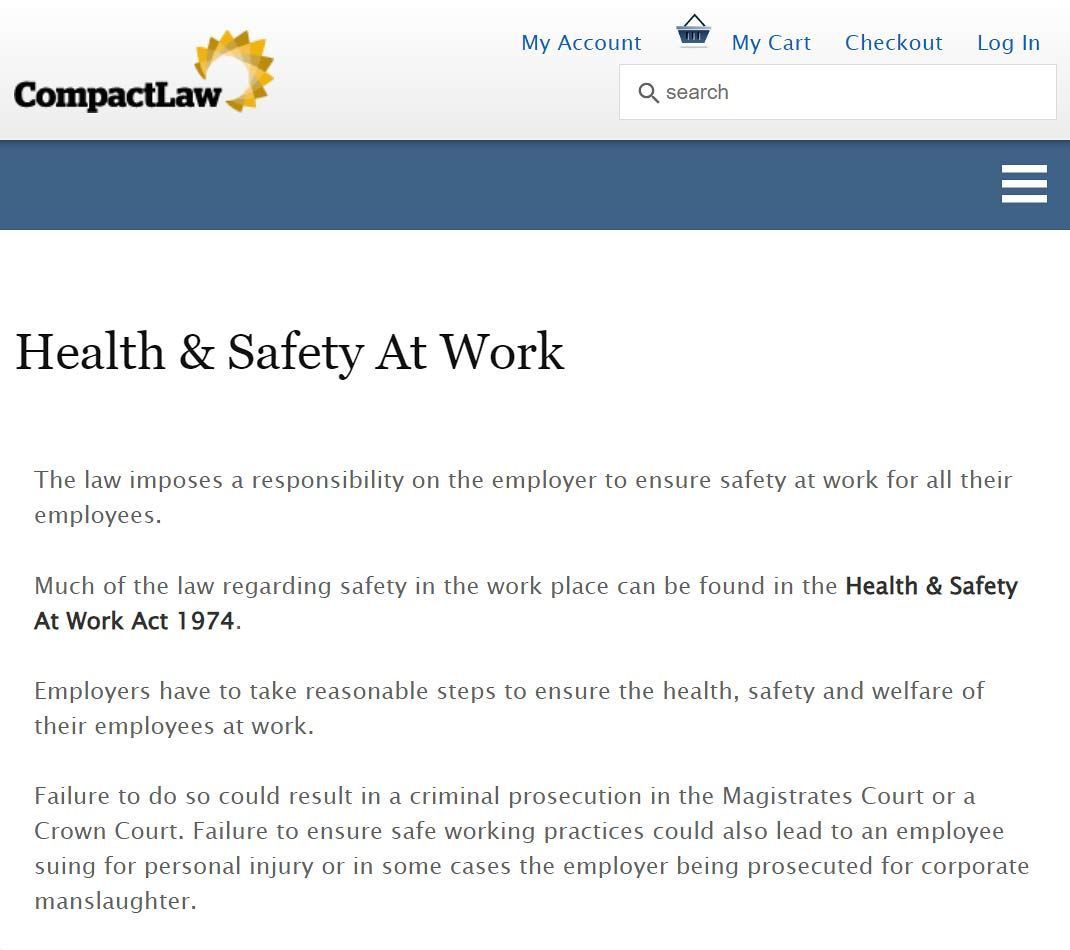
‘The law imposes a responsibility on the employer to ensure safety at work for all their employees.
Much of the law regarding safety in the work place can be found in the Health & Safety At Work Act 1974.
➲
Employers
have to take
reasonable steps to ensure the
health,
safety
and
welfare
of their employees at work.
Failure to do so could result in a criminal prosecution in the Magistrates Court or a Crown Court.
Failure to ensure safe working practices could also lead to an employee suing for personal injury or in some cases the employer being prosecuted for corporate manslaughter.
As well as this legal responsibility, the employer also has an implied responsibility to take reasonable steps as far as they are able to ensure the health and safety of their employees are not put at risk.
So an employer might be found liable for his actions or failure to act even if these are not written in law.
The employer’s responsibility to the employee might include a duty to provide safe plant and machinery and safe premises, a safe system of work and competent trained and supervised staff.
➲ Workplace (Health, Safety and Welfare) Regulations 1992:
This deals with any modification, extension or conversion of an existing workplace. The requirements include control of temperature, lighting, ventilation, cleanliness, room dimensions etc.
➲ Personal Protective Equipment Work Regulations 1992 (PPE):
Deals with protective clothing or equipment which must be worn or held by an employee to protect against health and safety risks.
It also covers maintenance and storage of such equipment.
Employers cannot charge for such clothing or equipment which must carry the “CE” marking.
➲ The employer may also have a responsibility to customers or visitors who use the work place.
It is always advisable for employers to have a written code of conduct, rules regarding training and supervision, and rules on safety procedures.
This should include information on basic health and safety requirements.
Leaflets and posters giving warnings of hazards are always advisable.
Also, the management of Health & Safety At Work Regulations 1992 requires an employer to carry out a risk assessment of the work place and put in place appropriate control measures.
➲ The Reporting of Injuries, Diseases and Dangerous Occurrences Regulations 1995 & 2013 (RIDDOR):
Employers must notify the Health and Safety Executive or local authority about work accidents resulting in death, personal injury or sickness where an employee is off work for more than 3 days.
Records must be kept of all such accidents at the workplace for at least 3 years.
Accident books must be kept where an employer employs ten or more persons on the same premises.
➲ Employers Liability (Compulsory Insurance) Regulations 1998
Employers must insure against liability for injury or disease sustained by an employee in the course of their employment.
The sum to be insured is not less than £5 million.’
❂
📖 (Accessed 4 Dec 2023 ~ Compact Law) Compact Law ~ Health & Safety At Work (Health & Safety At Work Act 1974) ➤
© 2023 Compact Law.
📖 (Accessed 4 Dec 2023 ~ Compact Law) Health & Safety At Work (Health & Safety At Work Act 1974) ➤
© 2023 Compact Law.
📖 (Accessed 4 Dec 2023 ~ UK Legislation Gov UK) Public General Acts / Health & Safety At Work Act 1974 ➤
© 2023 UK.GOV.