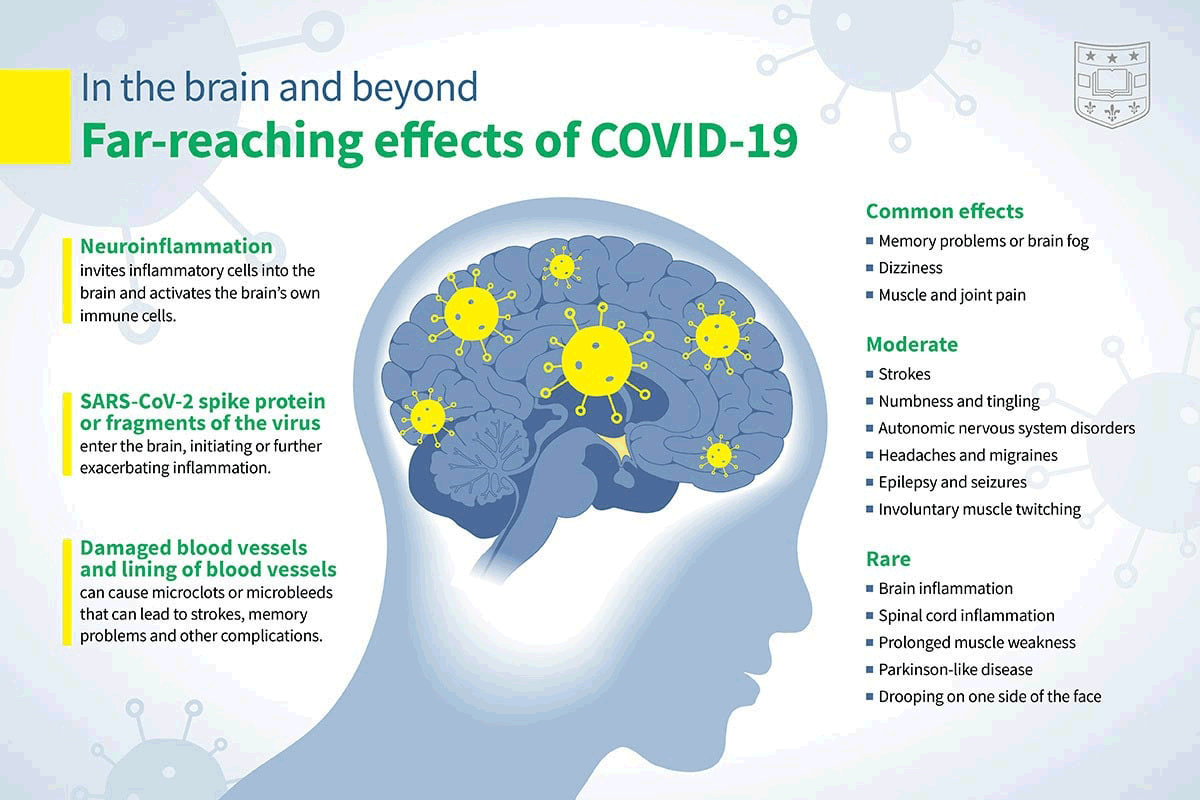
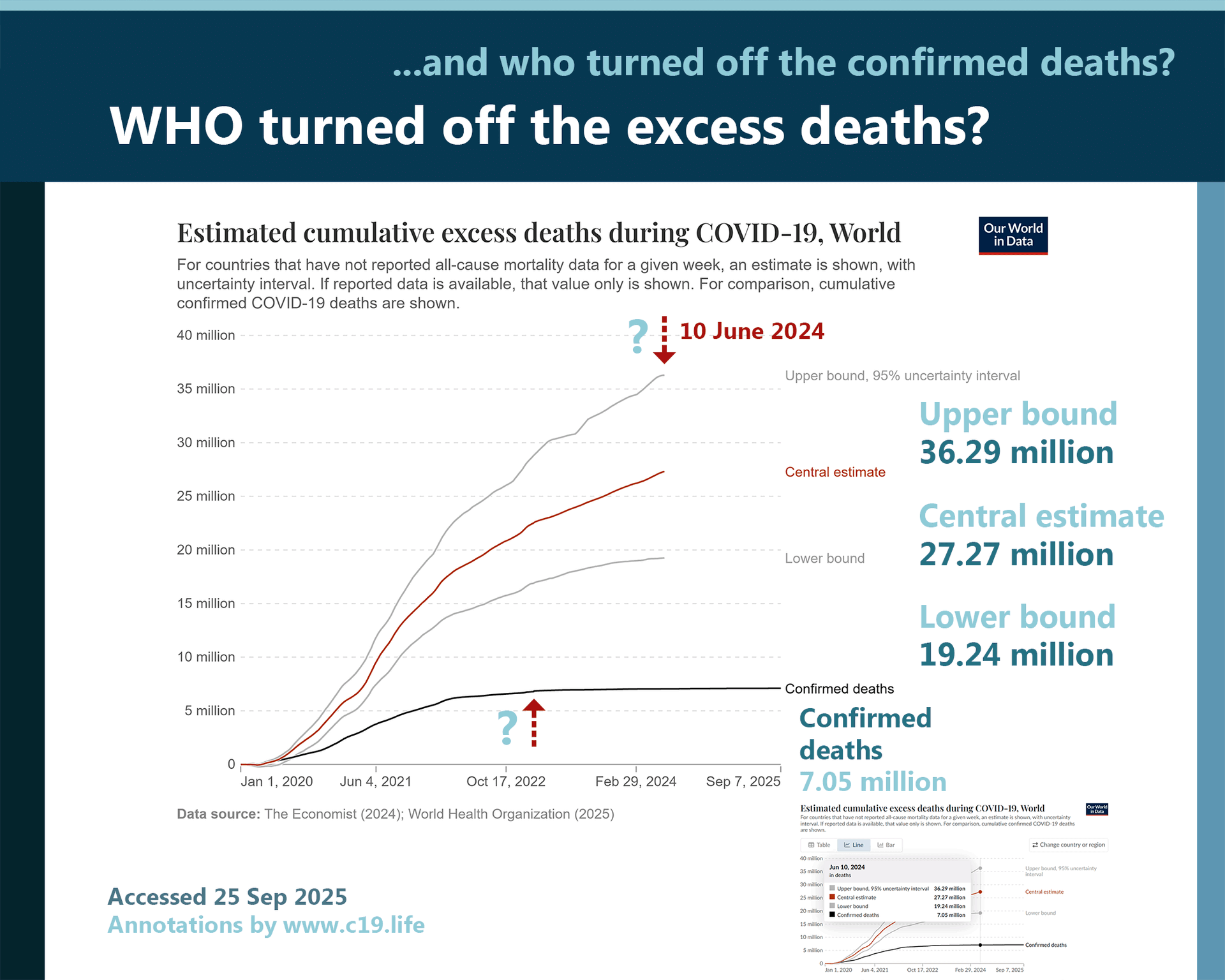
📖 COVID-19 disease and immune dysregulation
❦ While COVID-19 was originally characterized as hyperinflammatory in its pathophysiology, emerging evidence demonstrates the possibility of a strongly immunosuppressive phenotype in more critical disease states.
While immune activation from neutrophils and complement may contribute to inflammatory damage in the lungs, decreased antiviral responses, dysregulated macrophages and dendritic cells, and severe lymphopenia contribute to a suppressed state in which viral replication and secondary infections are prone.
❂
📖 (6 Dec 2022 ~ Best Practice & Research Clinical Haematology) COVID-19 disease and immune dysregulation ➤
© 2022 Davitt et al / Best Practice & Research Clinical Haematology.